Zabbix server is installable on any Linux distribution, but in this tutorial, I will show you step-by-step how to install and optimize the latest Zabbix 7 LTS release on Ubuntu 24.04 (Noble), 22.04 LTS (Jammy Jellyfish) / 20.04 (Focal).
Zabbix is 100% free open-source ultimate enterprise-level software designed for monitoring availability and performance of IT infrastructure components. You can read a case-study about Zabbix popularity and find out more about open-source movement in this article.
Enough of talk lets do some work! First, we will install and configure Zabbix server, then a database and lastly the frontend – check the picture bellow for a better understanding of Zabbix architecture.
This guide is for installing Zabbix monitoring system (Server) on Ubuntu, while guide for installing Zabbix-proxy on Ubuntu can be found on this link.
Table of Contents
- Step 1: Install Zabbix server, frontend, and agent
- Step 2: Configure database
- Step 3: Configure firewall
- Step 4: Start Zabbix server and agent processes
- Step 5: Configure Zabbix frontend
- Step 6: Login to frontend using Zabbix default login credentials
- Step 7: Optimizing Zabbix Server (optional)
- Step 8: Optimizing MySQL / MariaDB database (optional)
- Step 9: Create MySQL partitions on History and Events tables
- Step 10: How to manage Zabbix / MySQL / Apache service
- Step 11: Upgrade between minor versions
Step 1: Install Zabbix server, frontend, and agent
Note: You need to log in as a root user on your Linux server with “su -” or use “sudo” to successfully execute commands used in this tutorial.
Install Zabbix .deb package on your Ubuntu OS (24.04, 22.04, 20.04, 18.04 and 16.04 are supported).
Zabbix 7.0 LTS version (supported until June 31, 2029) wget https://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/7.0/ubuntu/pool/main/z/zabbix-release/zabbix-release_7.0-1+ubuntu$(lsb_release -rs)_all.deb sudo dpkg -i zabbix-release_7.0-1+ubuntu$(lsb_release -rs)_all.deb sudo apt update sudo apt -y install zabbix-server-mysql zabbix-frontend-php zabbix-apache-conf zabbix-sql-scripts zabbix-agent
You can find more information about Zabbix’s life cycle and release policies on the official website.
Step 2: Configure database
In this installation, I will use password rootDBpass as root password and zabbixDBpass as Zabbix password for DB. Consider changing your password for security reasons.
a. Install MariaDB 10.11
In your terminal, use the following command to install MariaDB 10.11 (supported untill 2028).
sudo apt install software-properties-common -y
curl -LsS -O https://downloads.mariadb.com/MariaDB/mariadb_repo_setup sudo bash mariadb_repo_setup --mariadb-server-version=10.11
sudo apt update sudo apt -y install mariadb-common mariadb-server-10.11 mariadb-client-10.11
NOTE: If you get error on Ubuntu 24.04: “The repository ‘https://dlm.mariadb.com/repo/maxscale/latest/apt noble Release’ does not have a Release file. [error] Failed to add trusted package signing keys” then use these commands instead of those above:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mariadb.list curl -fsSL https://mariadb.org/mariadb_release_signing_key.asc | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/mariadb-archive-keyring.gpg echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/mariadb-archive-keyring.gpg] https://dlm.mariadb.com/repo/mariadb-server/10.11/repo/ubuntu mantic main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list apt update apt install mariadb-server
Once the installation is complete, start the MariaDB service and enable it to start on boot using the following commands:
sudo systemctl start mariadb sudo systemctl enable mariadb
b. Reset root password for database
Secure MySQL/MariaDB by changing the default password for MySQL root, I will change it to “rootDBpass”:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
Enter current password for root (enter for none): Press Enter Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] y Change the root password? [Y/n] y New password: <Enter root DB password, I will set "rootDBpass"> Re-enter new password: <Repeat root DB password, I will set "rootDBpass"> Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]: Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]: Y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n]: Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]: Y
c. Create database
sudo mysql -uroot -p'rootDBpass' -e "create database zabbix character set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin;" sudo mysql -uroot -p'rootDBpass' -e "create user 'zabbix'@'localhost' identified by 'zabbixDBpass';" sudo mysql -uroot -p'rootDBpass' -e "grant all privileges on zabbix.* to zabbix@localhost identified by 'zabbixDBpass';"
d. Import initial schema and data.
Import database shema for Zabbix server (could last up to 5 minutes):
sudo zcat /usr/share/zabbix-sql-scripts/mysql/server.sql.gz | mysql --default-character-set=utf8mb4 -uzabbix -p'zabbixDBpass' zabbix
e. Enter database password in Zabbix configuration file
Open zabbix_server.conf file with command:
sudo nano /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf
and add database password in this format anywhere in file:
DBPassword=zabbixDBpass
Save and exit file (ctrl+x, followed by y and enter).
Step 3: Configure firewall
If you have a UFW firewall installed on Ubuntu, use these commands to open TCP ports: 10050 (agent), 10051 (server), and 80 (frontend):
ufw allow 10050/tcp ufw allow 10051/tcp ufw allow 80/tcp ufw reload
Step 4: Start Zabbix server and agent processes
sudo systemctl restart zabbix-server zabbix-agent sudo systemctl enable zabbix-server zabbix-agent
Step 5: Configure Zabbix frontend
a. Restart Apache web server and make it start at system boot
systemctl restart apache2
systemctl enable apache2
b. Configure web frontend
Connect to your newly installed Zabbix frontend using URL “http://server_ip_or_dns_name/zabbix” to initiate the Zabbix installation wizard.
In my case, that URL would be “http://192.168.1.161/zabbix” because I have installed Zabbix on the server with IP address 192.168.1.161 (you can find the IP address of your server by typing “ip a” command in the terminal).
Basically, in this wizard you only need to enter a password for Zabbix DB user and just click “Next step” for everything else. In this guide, I have used a zabbixDBpass as a database password, but if you set something else, be sure to enter the correct password when prompted by the wizard.

If you get the error “zabbix Locale for language “en_US” is not found on the web server. Tried to set: en_US, en_US.utf8, en_US.UTF-8, en_US.iso885915, en_US.ISO8859-1” then use this command to fix it:
apt-get install -y locales && echo 'en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8' >> /etc/locale.gen && locale-gen && service apache2 restart
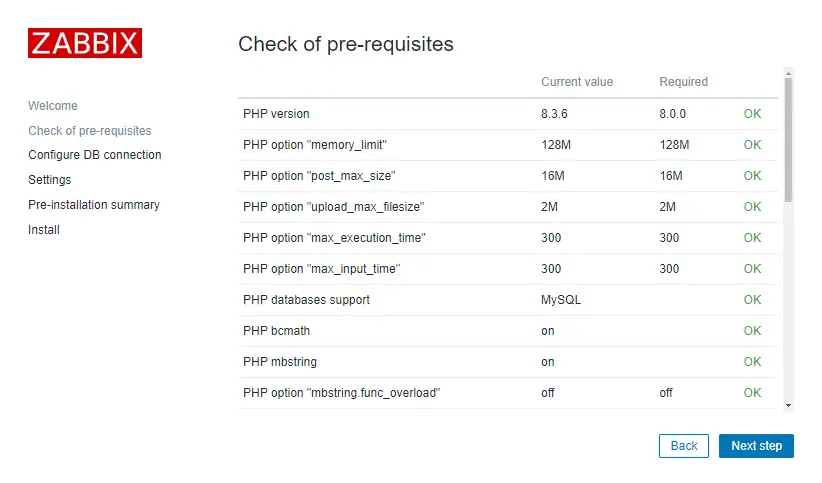
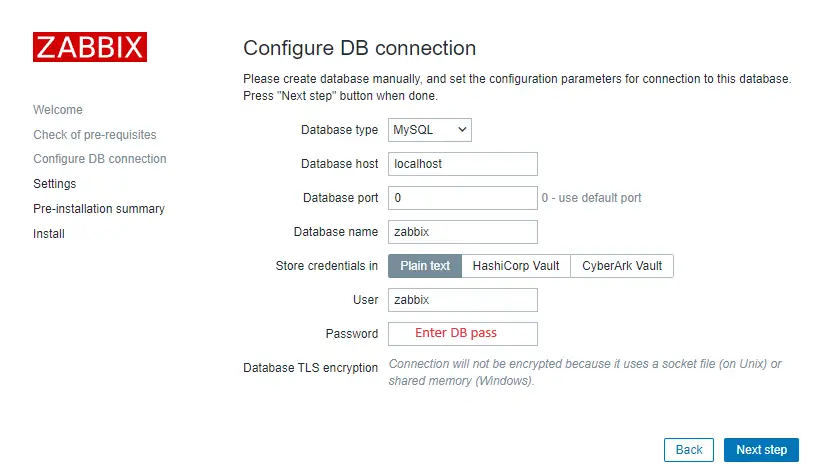
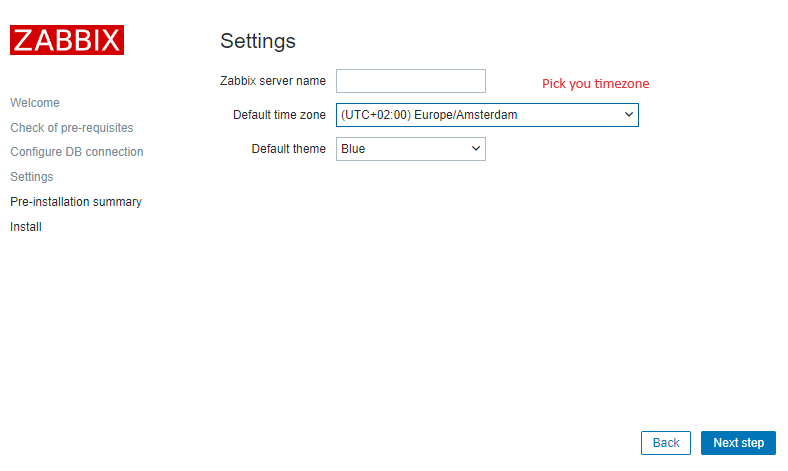
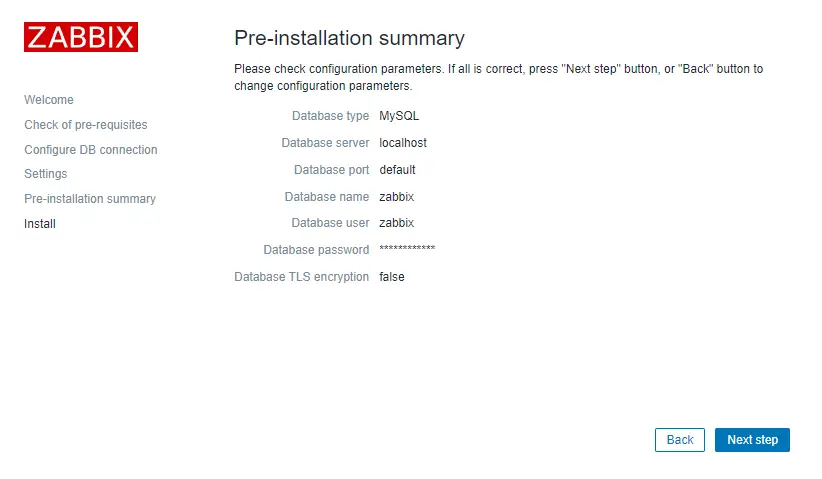
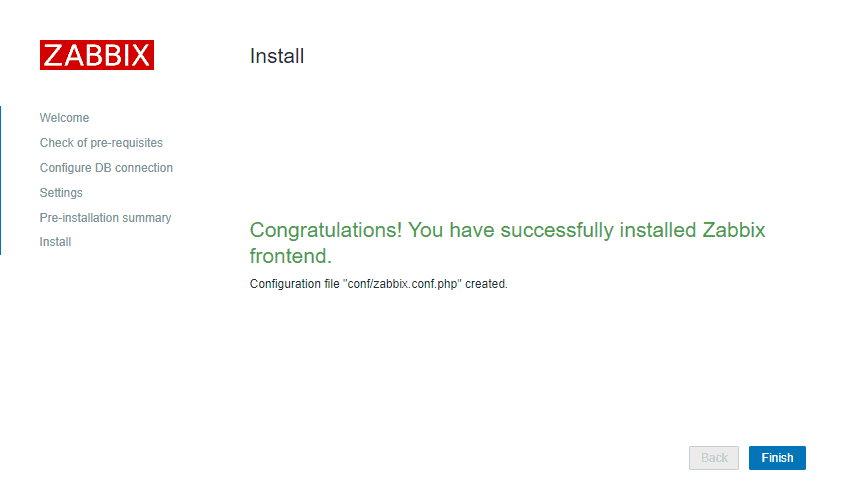
That’s it, you have installed Zabbix monitoring system!
Step 6: Login to frontend using Zabbix default login credentials
Use Zabbix default admin username “Admin” and password “zabbix” (without quotes) to login to Zabbix frontend at URL “http://server_ip_or_dns_name/zabbix” via your browser.

In my example, I have installed Zabbix on server 192.168.1.161 so I will enter in my browsers URL field http://192.168.1.161/zabbix (you can find the IP address of your server by typing “ip a” command in the terminal)
CONGRATULATIONS!
You have successfully installed Zabbix 7 on Ubuntu and now you can monitor anything!
No need to change anything else as other steps are optional.
CONTINUE TO LEARN MORE:
Optimizing Zabbix server and MySQL database
How to create MySQL partitions on History and Events tables
Managing Zabbix / MySQL / Apache service
Step 7: Optimizing Zabbix Server (optional)
Don’t bother with this optimization if you are monitoring a small number of devices, but if you are planning to monitor a large number of devices then continue with this step.
Open “zabbix_server.conf” file with command: “sudo nano /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf” and add this configuration anywhere in file:
StartPollers=100
StartPollersUnreachable=50
StartPingers=50
StartTrappers=10
StartDiscoverers=10
StartHTTPPollers=10
CacheSize=128M
HistoryCacheSize=64M
HistoryIndexCacheSize=32M
TrendCacheSize=32M
ValueCacheSize=256M
Save and exit file (ctrl+x, followed by y and enter).
This is not a perfect configuration, keep in mind that you can optimize it even more. Let’s say if you don’t use ICMP checks then set the “StartPingers” parameter to 1 or if you don’t use active agents then set “StartTrappers” to 1 and so on. You can find out more about the parameters supported in a Zabbix server configuration file in the official documentation.
If you try to start the Zabbix server you may receive an error “[Z3001] connection to database 'Zabbix' failed: [1040] Too many connections” in the log “/var/log/zabbix/zabbix_server.log” because we are using more Zabbix server processes than MySQL can handle. We need to increase the maximum permitted number of simultaneous client connections and optimize MySQL – so move to the next step.
Step 8: Optimizing MySQL / MariaDB database (optional)
a. Create custom MySQL configuration file
Create file “10_my_tweaks.cnf" with “sudo nano /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/10_my_tweaks.cnf” and paste this configuration:
[mysqld]
max_connections = 300
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 800M
innodb-log-file-size = 128M
innodb-log-buffer-size = 128M
innodb-file-per-table = 1
innodb_buffer_pool_instances = 8
innodb_old_blocks_time = 1000
innodb_stats_on_metadata = off
innodb-flush-method = O_DIRECT
innodb-log-files-in-group = 2
innodb-flush-log-at-trx-commit = 2
tmp-table-size = 96M
max-heap-table-size = 96M
open_files_limit = 65535
max_connect_errors = 1000000
connect_timeout = 60
wait_timeout = 28800
Save and exit the file (ctrl+x, followed by y and enter) and set the correct file permission:
sudo chown mysql:mysql /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/10_my_tweaks.cnf sudo chmod 644 /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/10_my_tweaks.cnf
Configuration parameter innodb_buffer_pool_size determines how much memory can MySQL get for caching InnoDB tables and index data. You should set that parameter to 70% of system memory if only database is installed on server.
However, in this case, we are sharing a server with Zabbix and Apache processes so you should set innodb_buffer_pool_size to 40% of total system memory. That would be 800 MB because my Ubuntu server has 2 GB RAM.
I didn’t have any problems with memory, but if your Zabbix proxy crashes because of lack of memory, reduce “innodb_buffer_pool_size” and restart MySQL server.
Learn more about database optimization in the tutorial: How to optimize Zabbix database?
b. Restart Zabbix Server and MySQL service
Stop and start the services in the same order as below:
sudo systemctl stop zabbix-server sudo systemctl stop mysql sudo systemctl start mysql sudo systemctl start zabbix-server
Step 9: Create MySQL partitions on History and Events tables
Zabbix’s housekeeping process is responsible for deleting old trend and history data. Removing old data from the database using SQL delete query can negatively impact database performance. Many of us have received that annoying alarm “Zabbix housekeeper processes more than 75% busy” because of that.
That problem can be easily solved with the database partitioning. Partitioning creates tables for each hour or day and drops them when they are not needed anymore. SQL DROP is way more efficient than the DELETE statement.
You can partition MySQL tables in 5 minutes using this simple guide.
Step 10: How to manage Zabbix / MySQL / Apache service
Sometimes you will need to check or restart Zabbix, MySQL or Apache service – use commands below to do that.
Zabbix Server sudo systemctl <status/restart/start/stop> zabbix-server MySQL Server sudo systemctl <status/restart/start/stop> mysql Apache Server sudo systemctl <status/restart/start/stop> apache2 Zabbix Agent sudo systemctl <status/restart/start/stop> zabbix-agent
Step 11: Upgrade between minor versions
I wrote about these upgrade procedures in my post about Zabbix upgrade. Zabbix’s team releases new minor versions at least once a month. The main purpose of minor upgrades is to fix bugs (hotfix) and sometimes even bring new functionality. Therefore, try to do a minor upgrade of Zabbix at least once a month.
There is no need for backups when doing a minor upgrade, they are completely safe. With this command you can easily upgrade smaller versions of 7.0.x (for example, from 7.0.1 to 7.0.3):
sudo apt install --only-upgrade 'zabbix*'
And restart Zabbix server afterward:
sudo systemctl restart zabbix-server



Please remove the versioning from the MariaDB install instructions. It generates an error and all you have to do is remove the 10.11.
hi
The problem can be fixed by modifying the right file:
nano /etc/dpkg/dpkg.cfg.d/excludes
and adding the following line about Zabbix
#… except zabbix
path-include=/usr/share/doc/zabbix*
Re-install the zabbix packages, and you should now see the file needed to continue
thanks to our friend
https://ogdenslake.ca/2021/03/03/zabbix-missing-mysql/
Wow ! Very good step-by-step instructions & very easy to follow 🙂
North Idaho Tom Jones
Hello,
Thank you so much for this manual !
Despite several installation attempts I always have the following message when I launch my web interface to finalize the installation : Access denied for user ‘admin’@’localhost’ (using password: YES)
And, I don’t undestand why zabbix account is created under “user.mysql” database instead of “users.zabbix” database after its creation ?.
Thank you in advance.
Hello good morning how are you?
So, I have a zabbix version 5.2.6, I installed a new version 6.2.3 on another server.. Is there a way to import the entire database from version 5.2.6 to 6.2.3???
Thanks.
Yes. Upgrade 5.2.6 to 6.2.3, dump DB to file, copy file to the new 6.2.3 server and import DB.
Hooray!! This is the only instruction that works. Thanks a lot.
Thanks for the post, I have the following query, I hope you can help me please.
I want to monitor 600 hosts, of which there will be approximately 28,000 triggers. I would like to know, based on your recommendation, what would be the best way to implement Zabbix, taking into account that it supports everything I want to monitor and gives it continuity.
An example could be to create 2 Ubuntu servers, the first for Zabbix server and Database (Main), the second for Zabbix proxy.
I will appreciate if you can help me. Thank you
You need a dedicated DB server, a good start would be 16G RAM and SSD. Zabbix server and frontend can be on the same server, that server doesn’t need a fast disk, just add at least 16G RAM. I think that 2 servers (DB & Server/Frontend) are enough for your environment. Later, you can always scale Zabbix and DB server vertically or add a proxy server if necessary.
Thank you, an excellent guide for a rookie. Can you help, i keep getting the following error during the import
Command:
sudo zcat /usr/share/doc/zabbix-sql-scripts/mysql/server.sql.gz | mysql -uzabbix -p’zabbixDBpass’ zabbix
Output:
/usr/share/doc/zabbix-sql-scripts/mysql/server.sql.gz: No such file or directory
When i browse to IP/zabbix/setup.php
Details Cannot connect to the database.
Unable to determine current Zabbix database version: the table “dbversion” was not found.
Zabbix changed the path to the SQL script files. Try again, I have updated the tutorial.
I have issue with:
gzip: /usr/share/doc/zabbix-sql-scripts/mysql/server.sql.gz: No such file or directory
Zabbix changed the path to the SQL script files. Try again, I have updated the tutorial.
Thanks for the guide. I have tried to install Zabbix 6.2 on ubuntu 22.04, and when I get to the install part I get an error or two. I have tried this with the guide on the zabbix site and same deal. Is there something I am missing?
sudo apt -y install zabbix-server-mysql zabbix-frontend-php zabbix-apache-conf zabbix-sql-scripts zabbix-agent
Reading package lists… Done
Building dependency tree… Done
Reading state information… Done
E: Unable to locate package zabbix-apache-conf
E: Unable to locate package zabbix-sql-scripts
Strange, I just tested on Ubuntu 22.04 and everything went without errors.
Eric,
got went through? let me know if something got to works for you.
hi
The problem can be fixed by modifying the right file:
nano /etc/dpkg/dpkg.cfg.d/excludes
and adding the following line about Zabbix
#… except zabbix
path-include=/usr/share/doc/zabbix*
Re-install the zabbix packages, and you should now see the file needed to continue
Thanks!
Thank you for this detailed guide, I tried zabbix official web site guide, but couldn’t succeed, This one got me in straight points. Thank you
Thank you very much,
With help of your Step by Step guidance, I successfully manage to install Zabbix
Hello Aldin,
I hopo you’re fine!
Your tutorial is perfect!
I managed to learn perfectly how to install Zabbix Server.
Congratulations on the excellent work.
Thanks,
Marcos
I am trying to create the db tables with Ubuntu 20.04 and Zabbix 5.4. This version doesn’t install the create.sql.gz scripts in /usr/share/doc/zabbix-server-mysql.
I had to install one additional packages: zabbix-sql-scripts which creates a directory /usr/share/doc/zabbix-sql-scripts, which has sub-directories under it and contains the needed sql scripts to setup the db.
The process need to be updated to include installing the extra package and also pulling the create.sql.gz from a different directory.
Thx for the info, I have updated the tutorial.
Has anyone gotten this to run on Ubuntu 21.04?
Hey everyone, hi.
I’m getting a bug from:
DateTime::__construct(): Invalid date.timezone value ‘Africa/Angola’, we selected the timezone ‘UTC’ for now.
I’m from Angola (country) and Africa as a continent.
“Africa/Angola” timezone is not supported, check out thise link: https://www.php.net/manual/en/timezones.africa.php
You need to use the Capital of Angola so for you that would be: Africa/Luanda
Thank you for this tutorial. It’s really clear and efficient.
Thank you for this guide, I managed to setup a zabbix container on proxmox, using this awesoem guide. Have a great day.
Very good tutorial!!!!
100% working!!!
Thank you so much.
Need open Firewall
ufw allow 80/tcp
ufw reload
Thx for information. I updated the tutorial
Hello
i’ve installed Zabbix server and proxy following this guides on Ubuntu desktop 20.04 but my proxy is not able to reach server.
i have this error in log and i can’t understand where i mistake.
this is log errors.
42255:20201219:220845.449 misconfiguration error: the proxy is running in the active mode but server at “127.0.0.1” sends requests to it as to proxy in passive mode
42250:20201219:220845.449 received configuration data from server at “127.0.0.1”, datalen 189
42256:20201219:220845.450 cannot send heartbeat message to server at “127.0.0.1”: empty string received
42250:20201219:220845.450 failed to update local proxy configuration copy: cannot open JSON object or array “”failed”,”info”:”misconfiguration error: the proxy is running in”
42257:20201219:220845.450 cannot send proxy data to server at “127.0.0.1”: empty string received
someone can help me?
Thanks
Flavio
You have misconfigured the proxy configuration on the Zabbix frontend. Select “active” instead of “passive” mode.
Very good, it worked 100% here
Centos 8
Iv used this article as a reference a few times and I greatly appreciate it, one thing iv managed to speculate on a few times is the following line.
“Don’t bother with this optimization if you are monitoring a small number of devices, but if you are planning to monitor a large number of devices then continue with this step.”
Now, since what a person considerins “a small number of devices” is very subjective, i was wondering if you could give some sort of indication when you would start optimizing.
I have a project in the works where 50-70 switches(mixed cisco/hp) and about 20+ varity of devices(controllers for 400+ access points) etc
Would you consider that a small or would you recommend optimizing? Despite the size it is pretty low in usage, so not a lot of traffic is generated.
Thanks for sharing a article 🙂
It’s hard for me to define a number of devices that would define a small environment because one device can have a thousand items or you can have a thousand devices with one item. However, if you only use the out-of-box templates from the Zabbix and you don’t have more than 30 devices I would call that a small environment, everything above that requires optimization of the Zabbix server and potentially the database.
thanks for the reply, it’s greatly appreciated!
Sir Thanks for such wonderful guideline to install Zabbix.
Installation done Perfectly but Zabbix Server is not running and getting error in
Administration -Queue –
Connection to Zabbix server “localhost” refused. Possible reasons:
1. Incorrect server IP/DNS in the “zabbix.conf.php”;
2. Security environment (for example, SELinux) is blocking the connection;
3. Zabbix server daemon not running;
4. Firewall is blocking TCP connection.
Connection refused
Please help.
Thanks
Check out my comment.
Not sure if it’s the right way to go about it but I fixed the “sudo mysql_secure_installation : command not found” problem by installing the mysql client & server with “sudo apt install mysql-server mysql-client”.
This appears to have worked although when I run the command, “sudo mysql_secure_installation” the response I get is:
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
Securing the MySQL server deployment.
Connecting to MySQL using a blank password.
VALIDATE PASSWORD COMPONENT can be used to test passwords
and improve security. It checks the strength of password
and allows the users to set only those passwords which are
secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD component?
Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: y
There are three levels of password validation policy:
LOW Length >= 8
MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters
STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file
Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG:
I killed that and tried again and was not asked about the “VALIDATE PASSWORD COMPONENT” and the rest followed your instructions provided up to the command:
sudo mysql -uroot -p’rootDBpass’ -e “grant all privileges on zabbix.* to zabbix@localhost identified by ‘zabbixDBpass’;”
The error was:
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
ERROR 1064 (42000) at line 1: You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ‘identified by ‘zabbixDBpass” at line 1
I used the same passwords as the instructions since this is just a test to see if I can get things working.
Thanks.
Looks like that you have installed a newer version of MySQL instead of MariaDB. In that case, is not necessary to put “identified by” part just “sudo mysql -uroot -p’rootDBpass’ -e “grant all privileges on zabbix.* to zabbix@localhost”;”
Thanks for the reply and explanation. I was running a VM so I just reverted and installed MariaDB. Everything works great. Awesome job!
When I execute the command: sudo mysql_secure_installation
I get an error: sudo: mysql_secure_installation: command not found
I checked the installation of the packages and to the best of my knowledge they installed:
sudo apt -y install zabbix-server-mysql zabbix-frontend-php zabbix-apache-conf zabbix-agent
Reading package lists… Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information… Done
zabbix-agent is already the newest version (1:5.0.3-1+focal).
zabbix-apache-conf is already the newest version (1:5.0.3-1+focal).
zabbix-frontend-php is already the newest version (1:5.0.3-1+focal).
zabbix-server-mysql is already the newest version (1:5.0.3-1+focal).
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
I previously set up Zabbix on a Raspberry Pi and everything worked really well, thanks for the great instructions and information.
Thanks
For some reason, Zabbix installation packages do not install MariaDB on Ubuntu 20.04. If you receive the error “mysql_secure_installation: command not found”, then you need to install MariaDB. I updated the tutorial, check out the section “Configure database”.
Thanks so much for the follow-up. I just built another instance on a Raspberry Pi and found the same problem which you have updated in your documentation. This did not happen a couple of weeks ago so I assume something [obviously] changed. No problem now that I know how to fix it.
Hi,
I am getting this error while sending a test email(gmail) notification:
Connection to Zabbix server “localhost” refused. Possible reasons:
1. Incorrect server IP/DNS in the “zabbix.conf.php”;
2. Security environment (for example, SELinux) is blocking the connection;
3. Zabbix server daemon not running;
4. Firewall is blocking TCP connection.
Connection refused
Following are the parameters of zabbix.conf.php
$ZBX_SERVER = ‘localhost’;
$ZBX_SERVER_PORT = ‘10051’;
$ZBX_SERVER_NAME = ‘ubuntu’;
what should i do? I tried changed from localhost to my internet/dns ip…still didn’t worked out. And also i didn’t found any process on 10051 port. the servername is my hostname.
Please help me out someone.
Check again file zabbix.conf.php
ZBX_SERVER = ‘**your zabbix ip address or DNS name**’;
ZBX_SERVER_PORT = ‘10051’;
ZBX_SERVER_NAME = ‘**your zabbix hostname**’;
After that, restart the Zabbix server.
If that doesn’t help, then disable the firewall and SELinux temporarily and restart the Zabbix server to see if that couses problem.
Thanks you for posting, followed instructions and up in running in no time.
Thanks for your walkthrough. Does this need any prerequisites, like apache or mariadb being installed first? I get stuck at step 4-a. /etc/zabbix/apache.conf does not exist, so I can’t edit the lines you mention.
Maybe you are viewing old tutorial from the cache that is missing “zabbix-apache-conf” parameter from step 1:
Just run the command:
sudo apt -y install zabbix-apache-conf
That seems to be exactly what happened. Works like a charm now. Thanks!